A razor-thin vote in favour of the EU’s nature restoration law on Monday has salvaged the bloc’s ability to restore its carbon sinks and reach its net zero goal, top officials told Climate Home.
The regulation, which tasks the EU’s 27 member states with reviving their land and water habitats and planting billions of trees, was narrowly passed by EU environment ministers.
The controversial law only gained enough backing because Austria’s minister for climate action, Leonore Gewessler, defied her country’s leader and voted in favour of it, a decision which may be challenged legally.
But, while celebrating the bill’s approval, climate campaigners and scientists warned that its ambition had been diluted and it must be implemented effectively to reverse the destruction of Europe’s natural carbon sinks.
EU warns “delaying tactics” have made plastic treaty deal “very difficult”
The law requires each EU country to rejuvenate 20% of their degraded land and water habitats by 2030 and all of them by 2050, and to plant three billion more trees across the bloc by 2030.
It also requires countries to restore 30% of their drained peatlands by 2030 and 50% by mid-century.
Peatlands that have been drained, largely for farming, forestry and peat extraction, are responsible for 5% of Europe’s total greenhouse gas emissions.
Climate breakthrough
Belgium’s climate minister Zakia Khatattabi told Climate Home that the law’s passing is “not only a breakthrough for nature but also for the climate”, and would enable the EU to meet its emissions-cutting targets.
Olivier De Schutter, the United Nations special rapporteur on extreme poverty and human rights, said that “without it, carbon neutrality in Europe would have been put beyond reach”.
The amount of carbon dioxide sucked in by Europe’s carbon sinks – including forests, peatlands, grassland, soil and oceans – has been falling since 2010. For forests, the World Resources Institute blames logging for timber and biomass and more wildfires and pests for the decline.
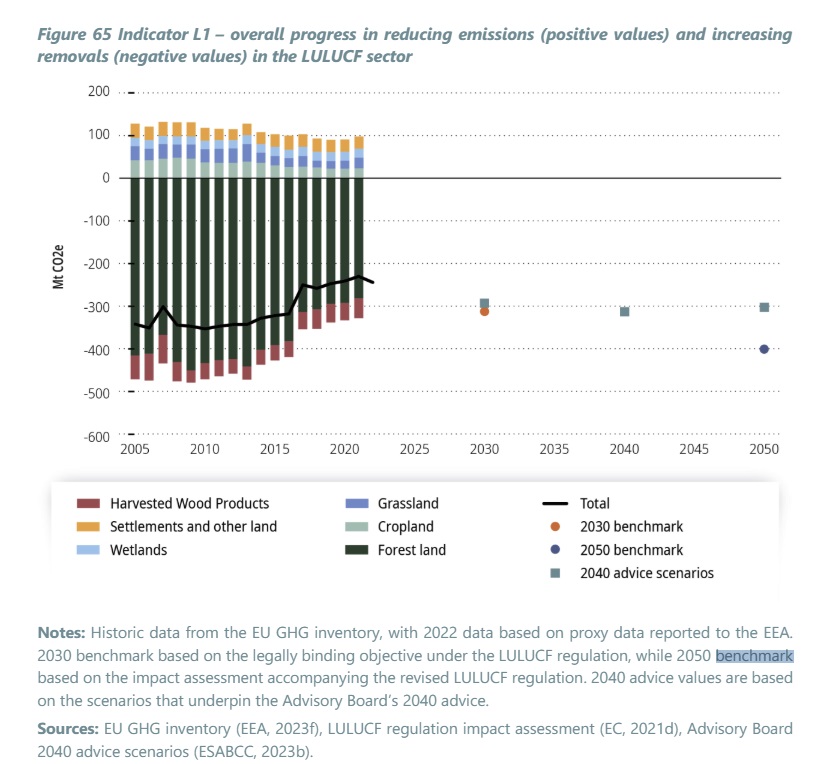
The amount of carbon sucked in is shrinking (black line) when it needs to increase to meet targets for 2030 (orange dot) and 2050 (blue dot)
But the EU’s plan to meet its goal of net-zero emissions by 2050 involves halting this decline and reversing it into a 15% increase on 2021 levels by 2030.
Jette Bredahl Jacobsen, vice-chair of the European Scientific Advisory Board on Climate Change, told Climate Home the new nature law “can contribute substantially to this, as healthy ecosystems can store more carbon and are more resilient against climate change impacts”.
The law is extremely popular with the EU public, with 75% of people polled in six EU countries saying they agree with it and just 6% opposing.
Watered down
But farmer trade associations were fiercely against it, and it became a symbolic battleground between right-wing and populist parties on one side and defenders of the EU Green Deal on the other.
Several of the law’s strongest passages ended up diluted before it reached ministers for approval, including caveats added to an obligation for countries to prevent any “net loss” of urban green space and tree cover this decade.
A new clause was introduced to deter EU states from using funds from the Common Agricultural Policy or Common Fisheries Policy to finance nature restoration – raising questions as to where money to implement the law will come from.
And, most importantly, an obligation to restore peatlands that have been drained for farming – a major source of emissions – was weakened.

A peat bog under restoration in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, pictured in January 2022. (Photo: Imago Images/Rüdiger Wölk via Reuters)
The original regulation would have instructed countries to rewet 30% of peatlands drained for agricultural use by 2030 and 70% by 2050 – the most effective way of restoring them.
But, as a concession to farmers, the final version of the nature law mandates rewetting just 7.5% of these peatlands by 2030 and 16.7% by 2050, with exceptions possible for actions such as replacing peatlands drained for agriculture with other uses.
Rewetting usually involves blocking drainage ditches. As well as reducing emissions, this helps an area adapt to climate change, protecting it from floods, and improving the water quality, soil and biodiversity.
But the Commission will also count other actions as peatland “restoration”, such as the partial raising of water tables, bans on the use of heavy machinery, tree removal, the reintroduction of peat-forming vegetation or fire prevention measures.
That’s despite the European Commission’s own rulebook describing these measures as “supplementary to gain better results” and saying that “peatland restoration should always primarily focus on rewetting”.
Lessons from trade tensions targeting “overcapacity” in China’s cleantech industry
Where rewetting does take place, as with all restoration measures in the final version of the regulation, EU states will be obliged to prioritise action in particular areas known as Natura 2000 sites. These cover around 18% of the EU’s territory, and should already have been restored under existing legislation.
Environmentalists maintain that the legislation still has tremendous potential, pointing to possible actions such as the restoration of seagrass meadows which cover less than 0.1% of the ocean floor but absorb more than 10% of its carbon.
EU countries will now draft national nature restoration plans over the next two years showing how they intend to meet their targets, for assessment by the Commission.
(Reporting by Arthur Neslen; editing by Joe Lo and Megan Rowling)
