The livestock industry is essential for food security and economic development, according to a draft report by the United Nations’ Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) that reinforces its defence of practices in the emissions-heavy sector in recent years.
Former and current FAO officials and academics have criticised the document, seen by Climate Home News, for pro-industry bias, cherry-picking data and even “disinformation” about the environmental impacts of animal farming.
The FAO told Climate Home that a final version of the report – part of an assessment consisting of various documents – would be launched in 2025 and that conclusions should not be drawn from the draft text at this stage.
Estimates of livestock’s contribution to greenhouse gas emissions vary, ranging from 12%-20% of the global total – mostly in the form of methane from ruminants like cows and sheep, and carbon dioxide (CO2) released when forests are cut down for pasture.
Methane, which is emitted in cow burps and manure, is a short-lived greenhouse gas that is 84 times more potent than CO2 over 20 years, making it one of the few available levers to prevent climate tipping points being reached in the near term.
In a 2024 survey of more than 200 scientists and sustainable agriculture experts, about 78% said livestock numbers should peak globally by 2025 to start bringing down emissions and help keep global warming to internationally agreed limits.
But the FAO’s draft study offers strong support for growth of the sector, saying livestock’s contributions to food security, nutrition and raw materials for industry make it a “linchpin for human well-being and economic development”.
It is also described as “critical” for food security, “crucial” for global economies, and “indispensable” for development in sub-Saharan Africa.
The report will be submitted to the FAO’s agriculture committee, which has 130 member nations, although the text could change as national representatives thrash out a final version.
Private-sector lobbyists participating as advisors in national delegations are sometimes also able to influence texts under discussion, according to a July report by the Changing Markets Foundation.
One FAO insider, who did not want to be named, told Climate Home the draft FAO report had been “biased towards pushing livestock [with] many national interests behind it”.
The FAO receives around a third of its budget in direct donations from member countries, and the rest in voluntary contributions from the same states and other actors, including businesses and trade associations.
Tech fixes
The 491-page draft report, which was overseen by a scientific advisory committee of 23 experts and peer reviewers, does not assess how diets with more plant protein could improve food security.
One advisory committee member, Professor Frederic Leroy of Vrije Universiteit Brussel, told Climate Home a shift to entirely plant-based diets “would severely compromise the potential for food security worldwide because many of the food nutrients which are already limited in global diets are found in livestock. How much you can move (away from livestock) should be the real investigation.”
This table from a World Bank report (Recipe for a Livable Planet), published in May 2024, shows that vegan diets are the lowest in emissions (Screenshot/World Bank)
The report’s analysis assumes rising meat production as demand surges among a growing world population with higher incomes. In this context, it proposes “expanding the (livestock) herd size”, increasing production through intensified systems, better use of genetic techniques, and improved land management.
“Technological innovations” such as feed additives and supplements to suppress methane are another idea backed by the FAO. Those could include experimental methods such as a vaccine announced last week and funded by a $9-million grant from the Bezos Earth Fund that aims to reduce the number and activity of methane-producing microbes in a cow’s stomach.
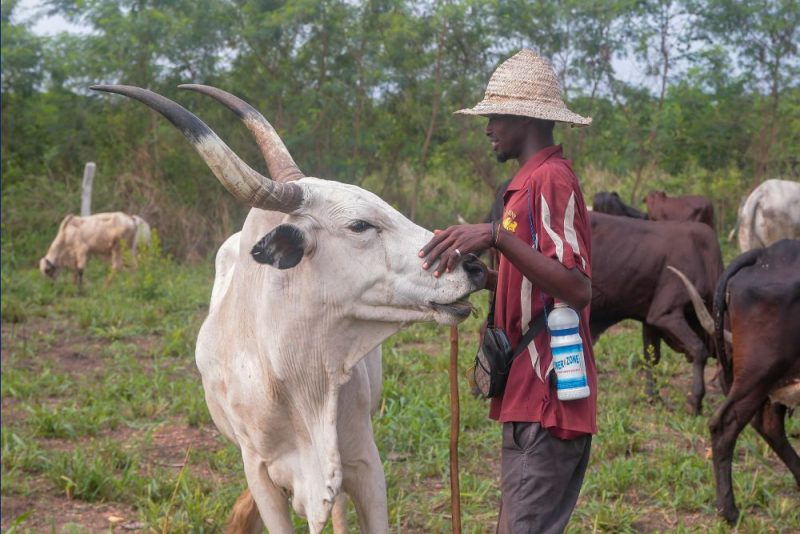

Herdsman Musa takes cattle to graze along the Dodowa-Somenya road in Ghana, April 12, 2024. According to environmentalist Kwame Ansah, ‘The unchecked grazing is not only destroying crops but also eroding soil fertility exacerbating land degradation.’ (Photo: Matrix Images/Christian Thompson/via Reuters)
The report’s findings, once approved, will be fed into a three-part roadmap for bringing agricultural emissions in line with the Paris Agreement goal of limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
The first instalment, published at the COP28 climate summit, was viewed internally by some FAO experts as a generic placeholder which largely followed an industry-friendly agenda.
One ex-FAO official, who requested anonymity, told Climate Home the latest draft report on livestock ploughs a similar furrow and would set expectations for part two of the 1.5C roadmap.
“The reality is that if they do a (nearly) 500-page report and put 23 experts’ names in front of it, it’s to impress you and say: ‘This is what is going to happen. We’re going to defend the sector’,” the former UN official said.
Making the case for meat
The expert added that the study’s panel was skewed toward intensified livestock systems and had “cherry picked” evidence to justify recommendations pointing in that direction.
Several of the report’s advisory committee members have previously advocated for meat-based diets, and 11 of the study’s contributors work for the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), including one of the paper’s committee advisors.
According to the ex-FAO official, ILRI “has been pushing intensified livestock all its life. It’s their identity. It’s what they do.”
The institute co-founded an agribusiness-backed initiative – Pathways to Dairy Net Zero (P2DNZ) – which de-emphasised livestock emissions, framing them as just one of several problems for the industry to tackle.
ILRI did not respond to a request for comment.
IPCC’s input into key UN climate review at risk as countries clash over timeline
Shelby C. McClelland, of New York University’s Center for Environmental and Animal Protection, told Climate Home she was shocked by a repeated claim in the draft FAO report of “a lack of consensus among scientists regarding the contribution of livestock to global greenhouse gas emissions”.
“This downplays and outright ignores overwhelming scientific evidence from the IPCC [Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change], high-profile papers, and other recent studies,” McClelland said. “A statement like this in a supposedly scientific and evidenced-based review by the UN FAO is alarming given their influence on agenda-setting for global climate action.”
Advisory committee member Leroy countered that it was “dangerous” to talk about a scientific consensus when the metrics used to measure methane compared to other greenhouse gases are constantly evolving.
“This should be part of an open and transparent debate,” he added. “I don’t think we have reached consensus on the way we interpret the effects of livestock agriculture on climate change, the degree of it, how we can measure it and how we can deal with it.”
Scientists at the FAO first alerted the world to the meat industry’s climate footprint when they attributed 18% of global emissions to livestock farming in the seminal 2006 study, Livestock’s Long Shadow. This analysis found that, far from enhancing food security, “livestock actually detract more from total food supply than they provide.”
However, the paper sparked a backlash felt by key experts in the agency’s Rome headquarters, as the FAO hierarchy, industry lobbyists and state donors to its biannual $1-billion budget exerted pressure for a change of direction.
By the time of last December’s COP28, the FAO’s stance had shifted so far that two experts cited in another livestock emissions study called publicly for its retraction. They argued it had distorted their work and underestimated the emissions reduction potential from farming less livestock by a factor of between 6 and 40.
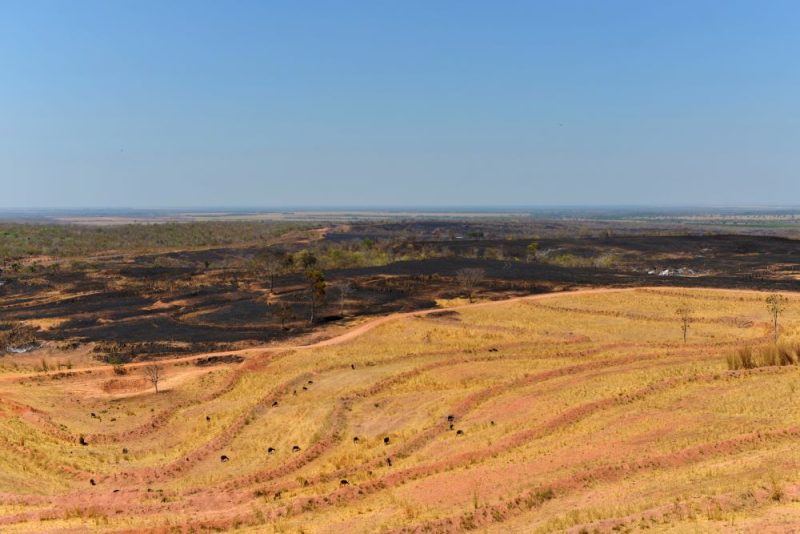

A deforested and burnt area is seen in an indigenous area used as cattle pasture in Areoes, Mato Grosso state, Brazil, September 4, 2019. (Photo: REUTERS/Lucas Landau)
No ‘carte blanche’
Guy Pe’er, a conservation ecologist at the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research and the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research, accused the FAO of turning a blind eye to widespread “hyper-intensive grazing practices” and land use change caused by the world’s growing number of mega-farms.
“We’re currently using more land to feed livestock than humans, and that is causing rapid deforestation in Brazil. Ignoring that is outrageous. When an official organisation is producing disinformation like this, I find it extremely irresponsible,” he said.
Leroy told Climate Home that different types of livestock farming should not be conflated. “If you have over-grazing and the pollution of water sources, that’s clearly wrong, but other types of animal agriculture are also net-positive [for the environment],” he said.
If the advisory committee “sees advantages in having livestock agriculture as part of the food system, I think there’s a sound scientific basis to assume that,” he added. “It doesn’t mean that it’s carte blanche or ‘anything goes’ at all.”
(Reporting by Arthur Neslen; editing by Megan Rowling and Joe Lo)
